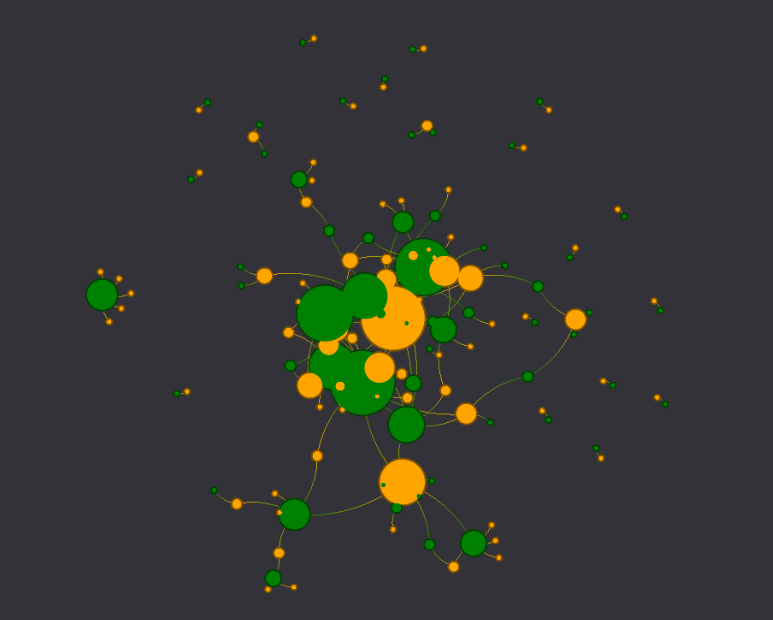
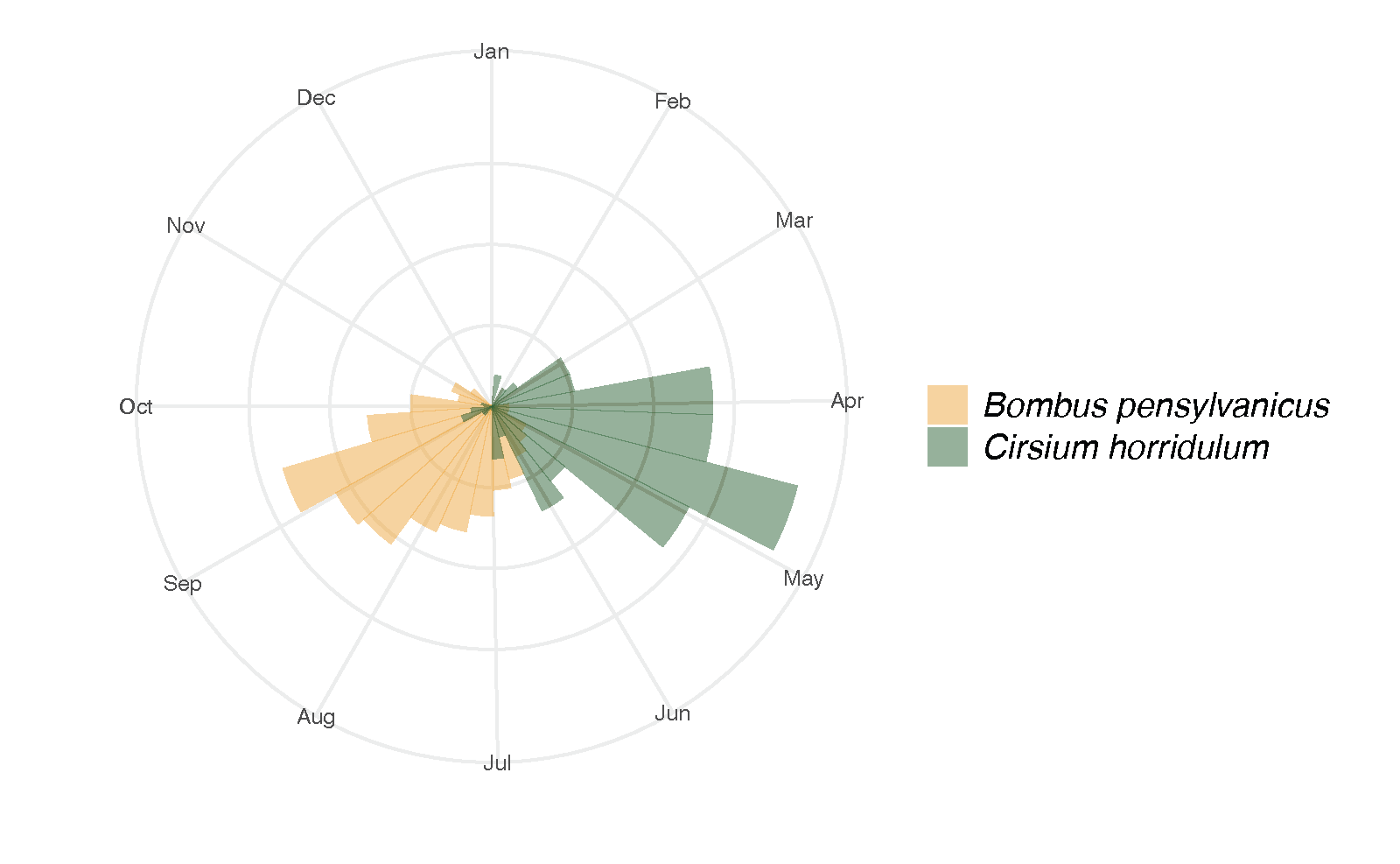
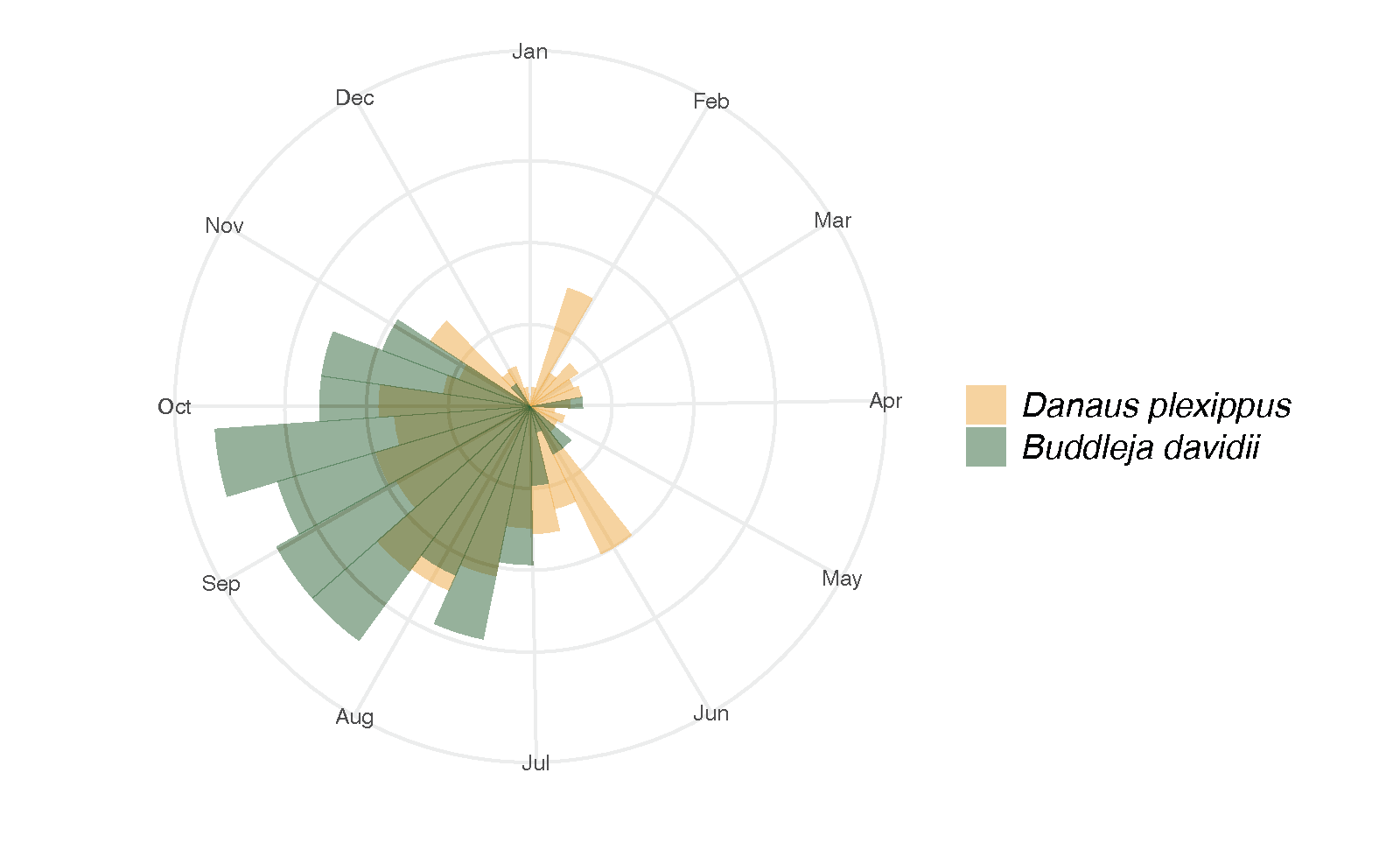
iNaturalist images with plants and pollinators
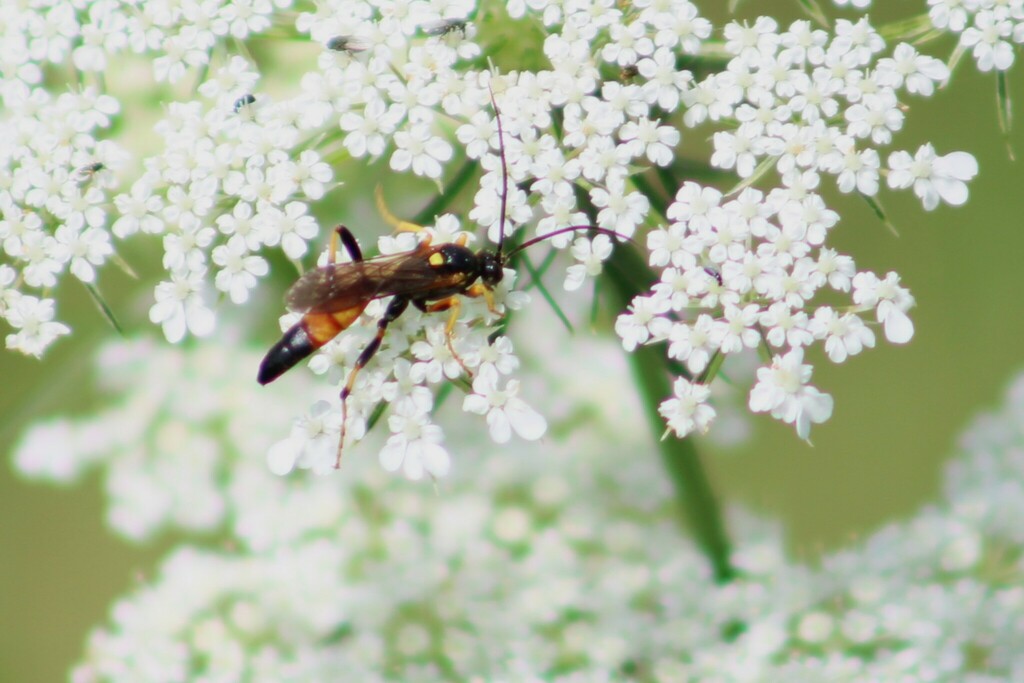

An Ichneumon wasp (Ichneumon annulatorius) visiting a wild carrot (Daucus carota) (Source).
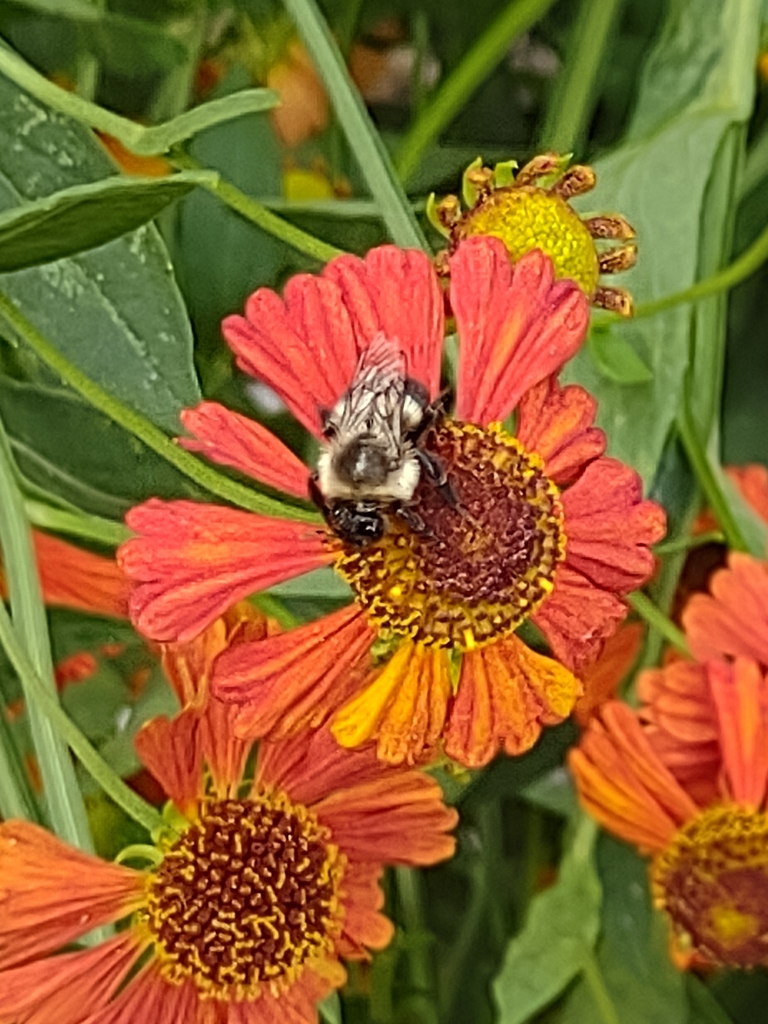

A common Eastern bumble bee Bombus impatiens visiting an unlabeled flowering plant (Source).