Highlights
- We identified macrophyte species for restoration of tropical reservoirs.
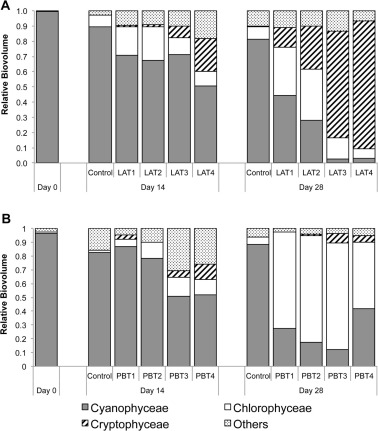
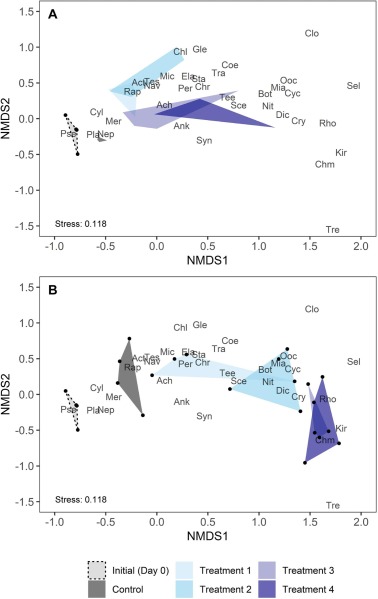
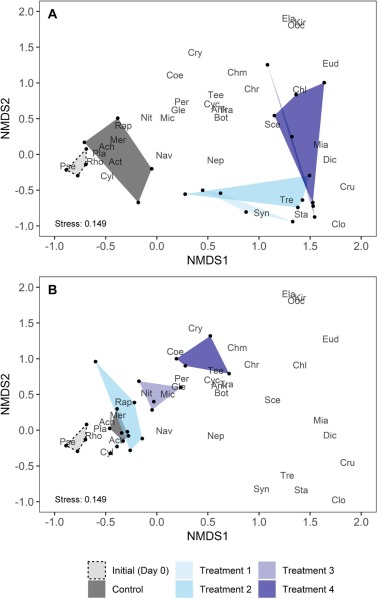
- All six species reduced cyanobacteria and increased cryptomonads at high density.
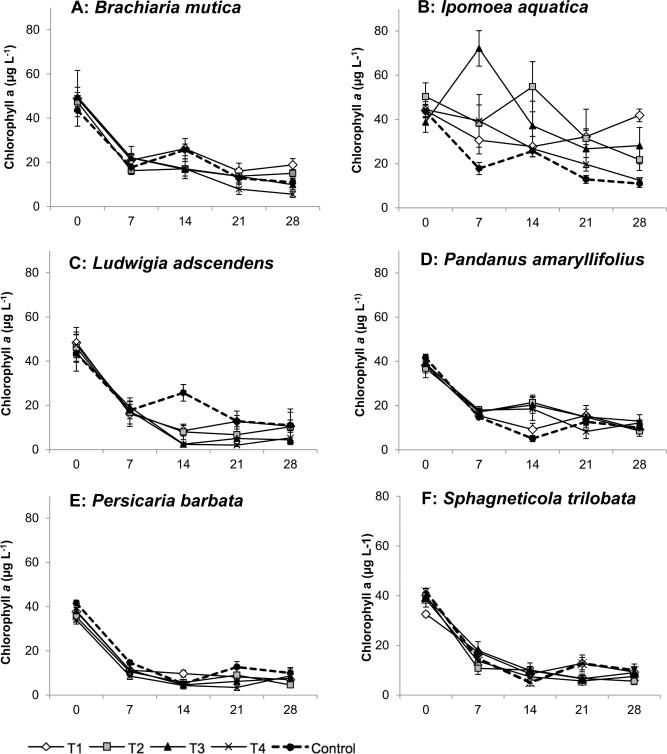
- Ludwigia adscendens and Persicaria barbata reduced chlorophyll a concentrations.
- Effective densities were found to be above 0.40 dry weight g/L.